Multi-Factor Authentication
To bind proofed identities to credentials for initial and subsequent authentication, ID.me offers a state of the art Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) suite that is certified to NIST 800-63-3B Authenticator Assurance Level (AAL) 2. These authenticator options provide a high level of confidence (Assurance Level 2) that the same user who was proofed remains in control of their account and credential.
ID.me’s MFA options play a crucial role in preventing fraud by adding a layer of security beyond just a username and password. ID.me offers several MFA options increasing accessibility for all demographics. For example, ID.me offers Call to Landline MFA for users without a cell phone and “unphishable” options such as a FIDO2 token the user carries with them on their keychain.
By doing so, ID.me’s MFA options, as highlighted below, reduce the risk of fraudulent access even if one factor, such as a password, is compromised.
When to use this policy
Ideal for integrations with an existing login that leverage multi-factor authentication.
Who is eligible?
Anyone with an ID.me account.
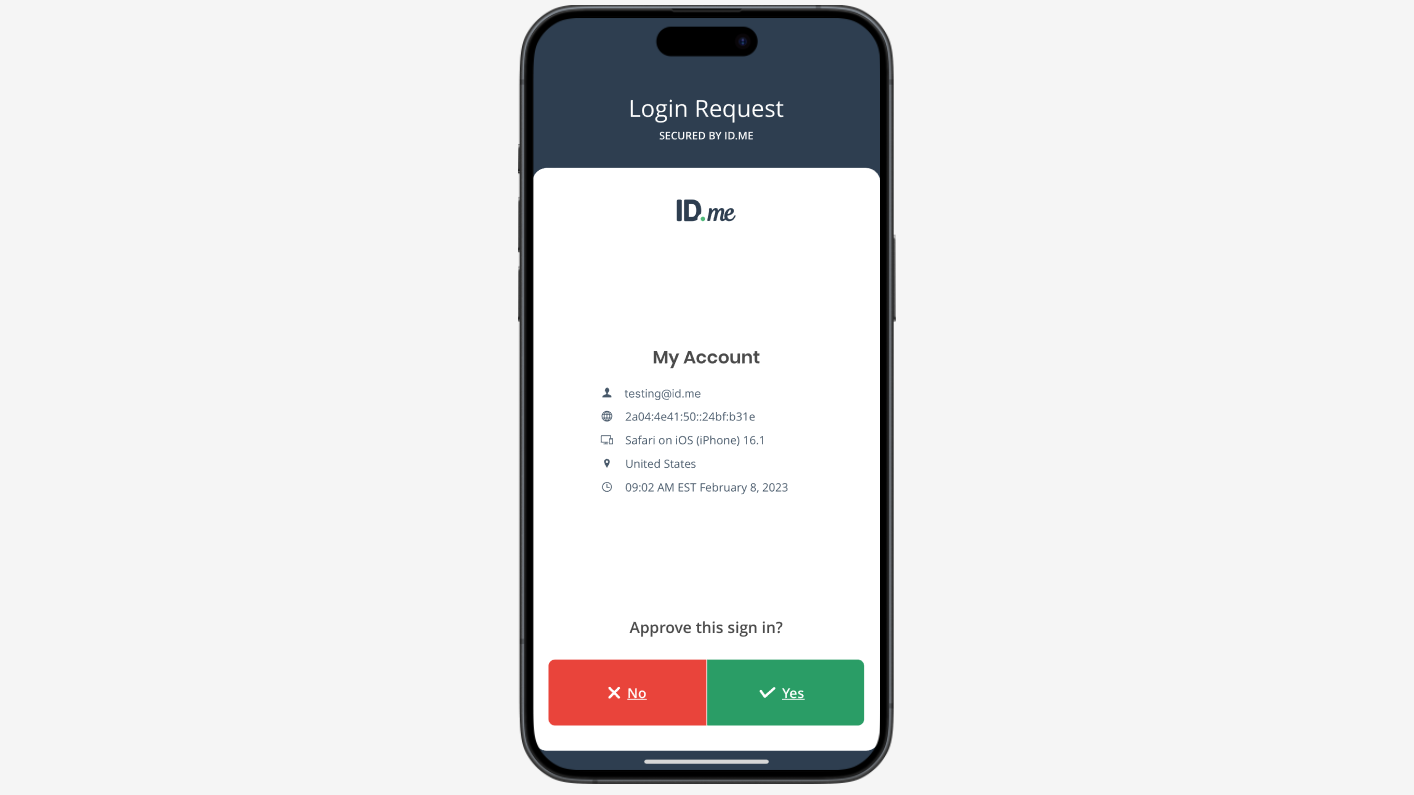
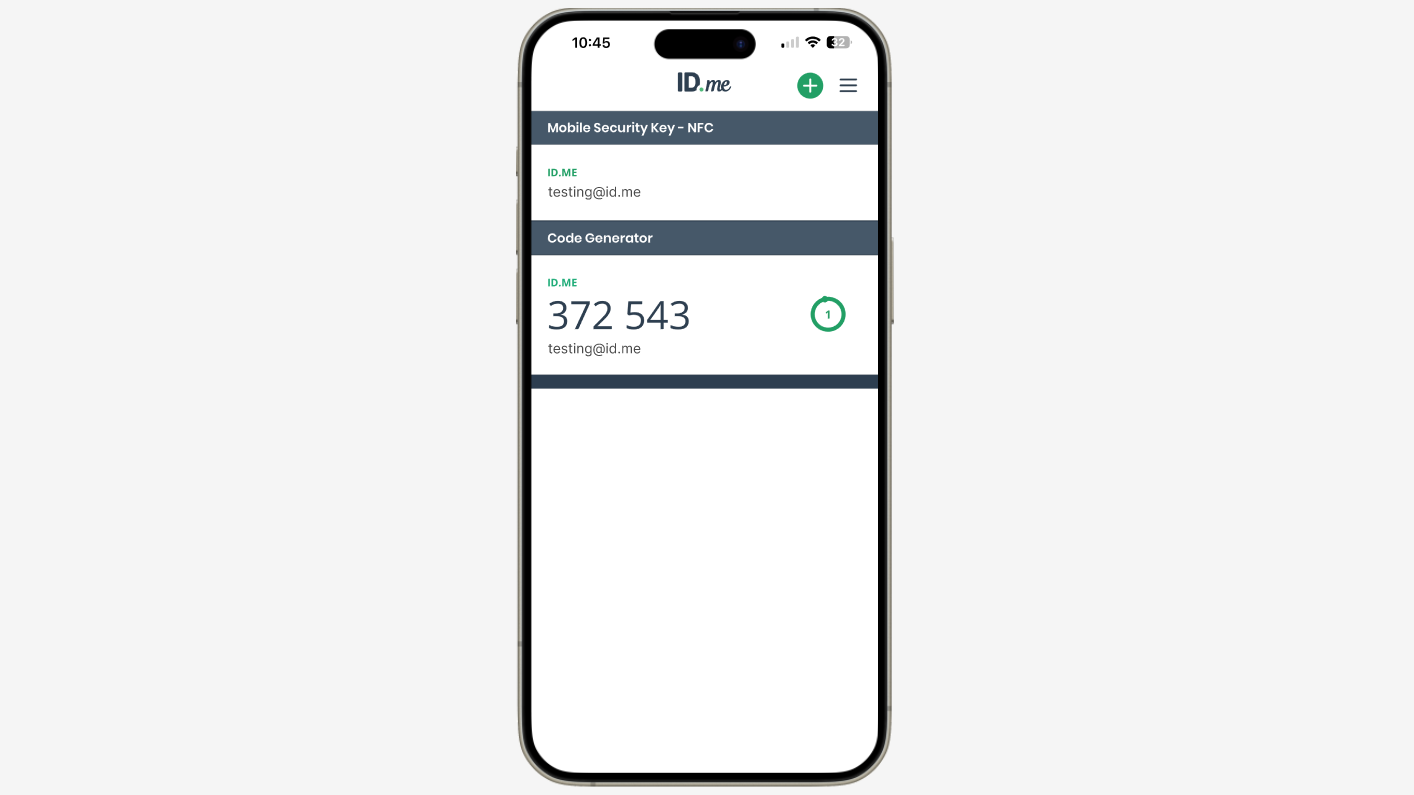
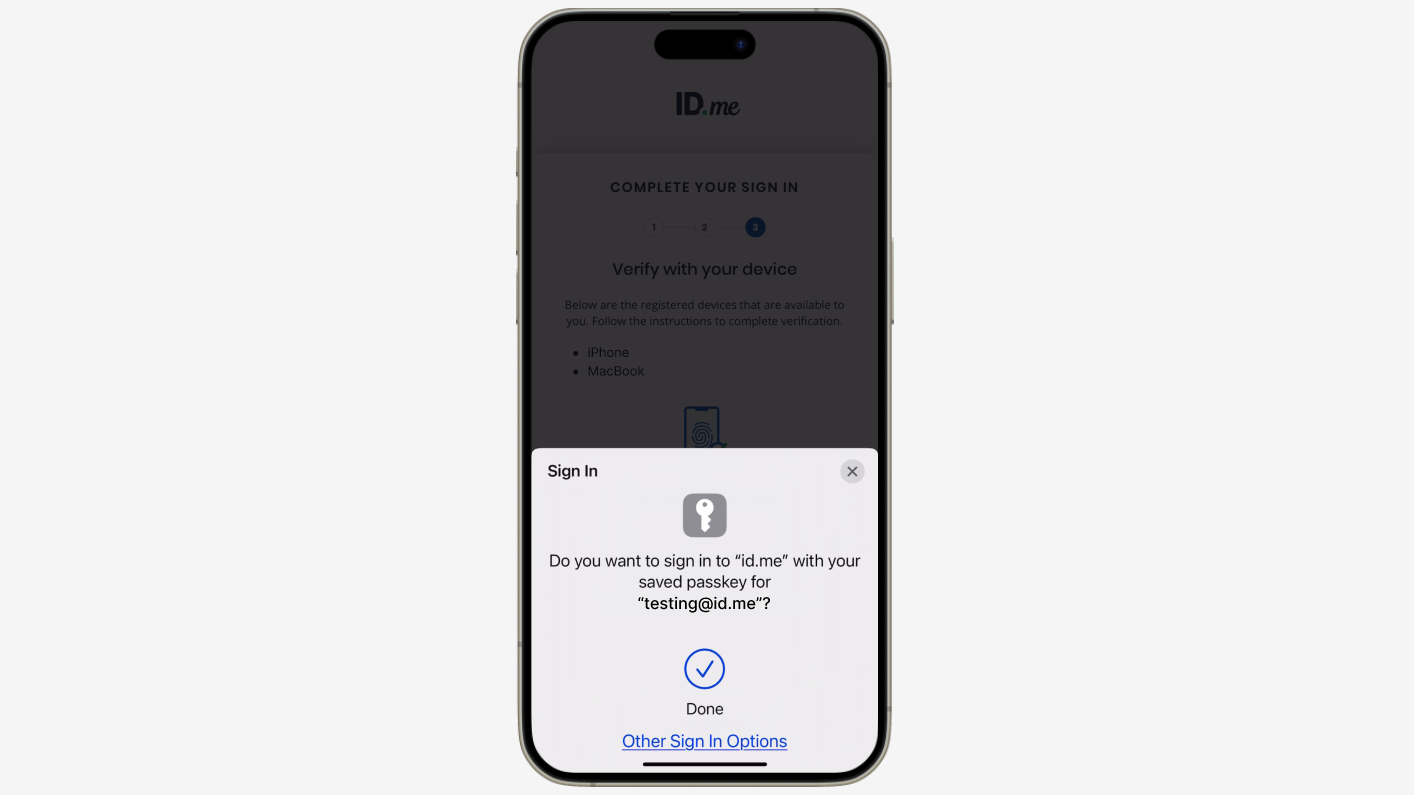
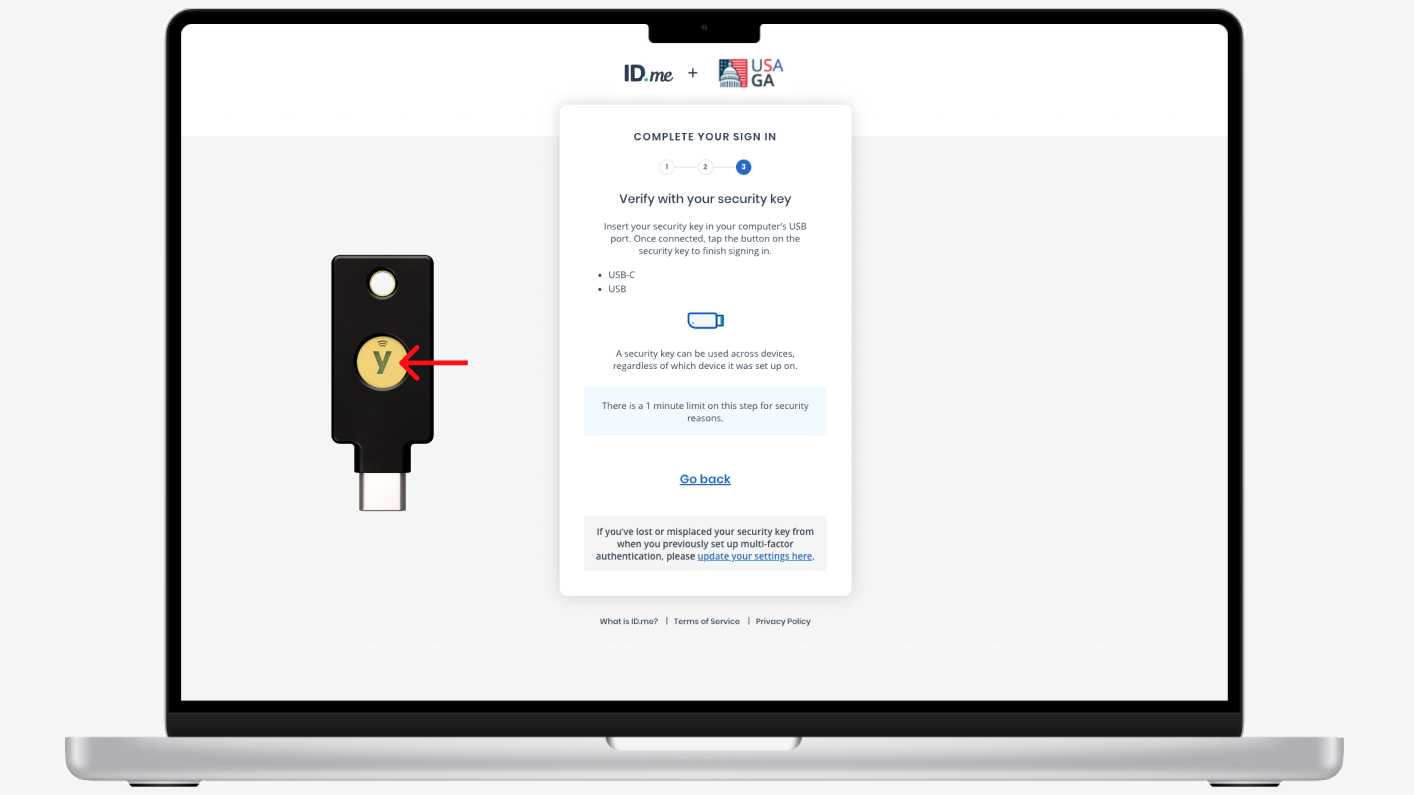
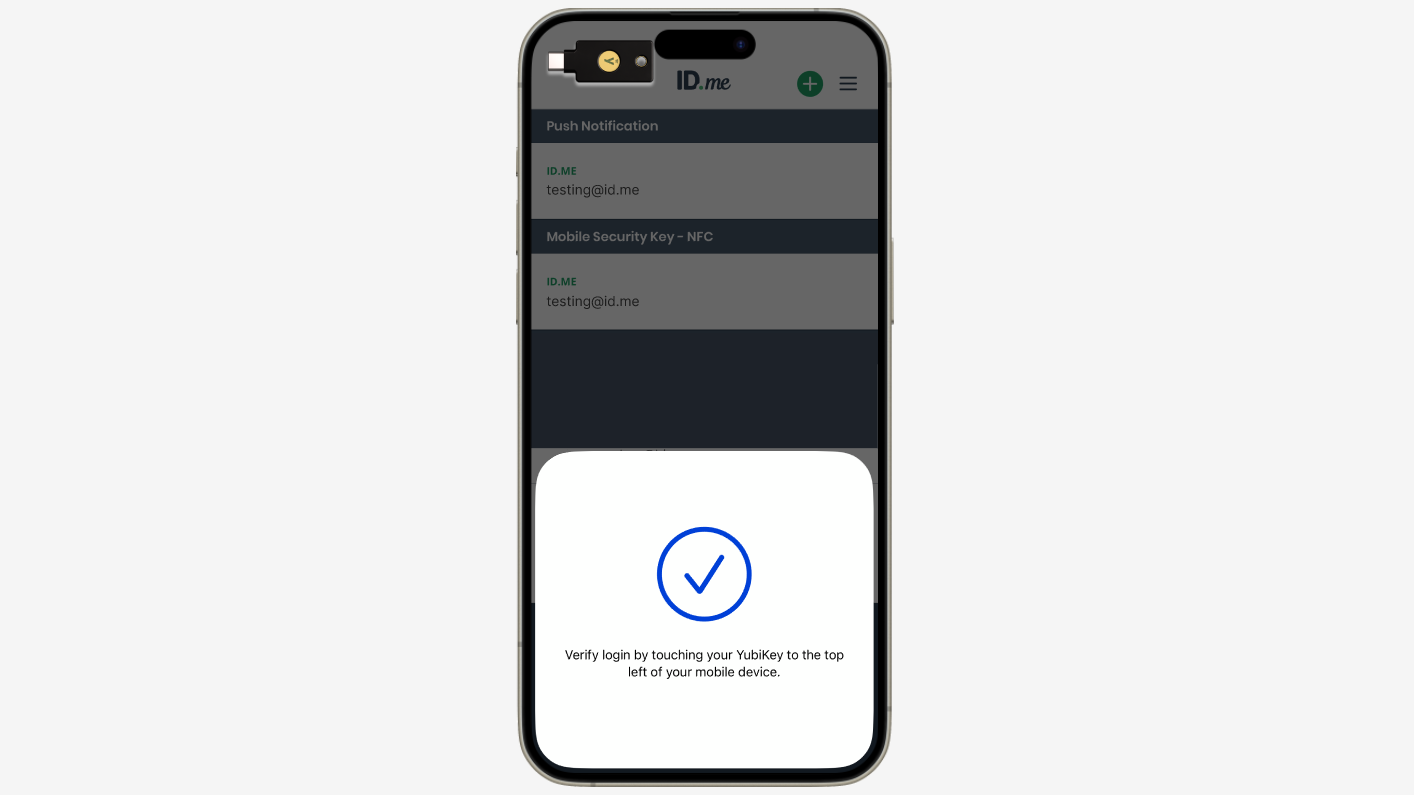
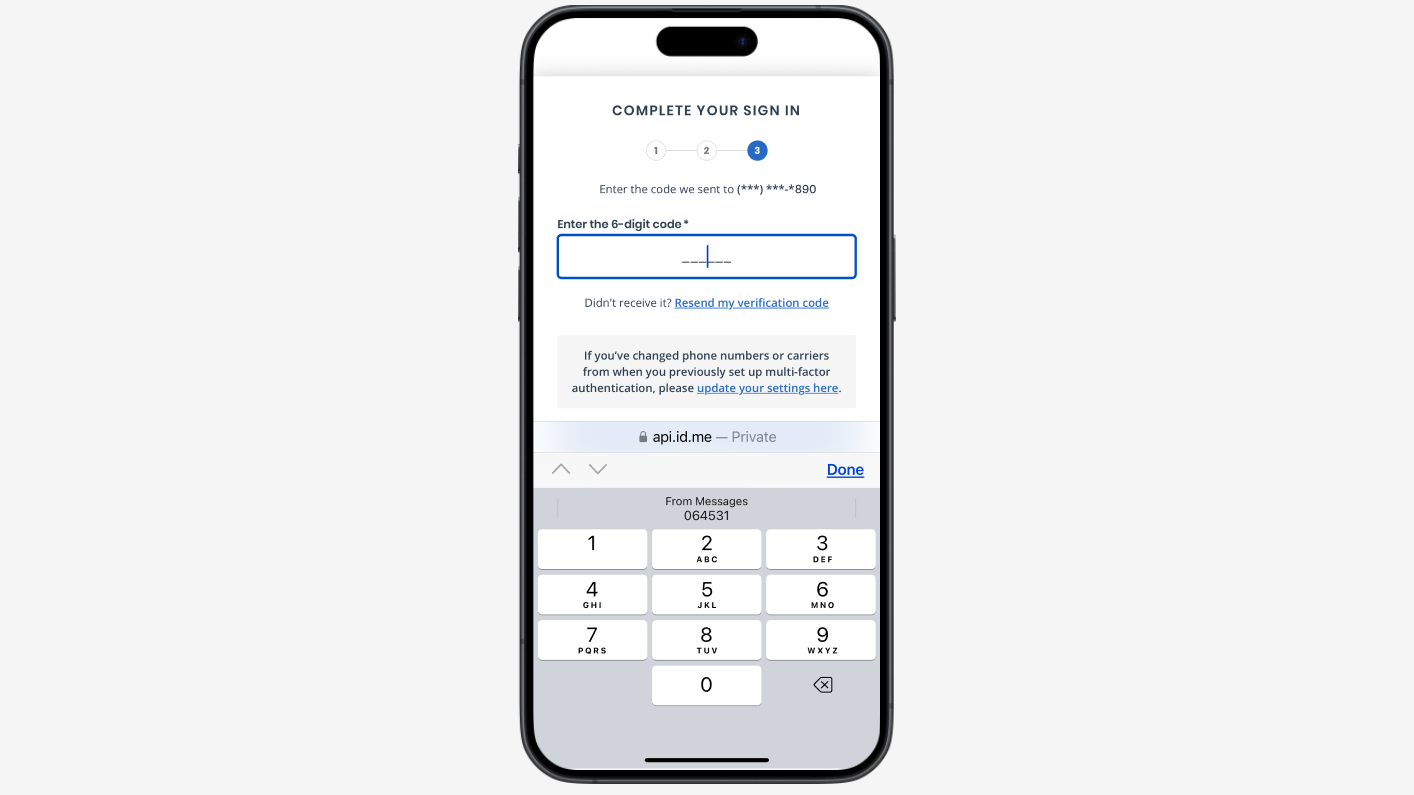
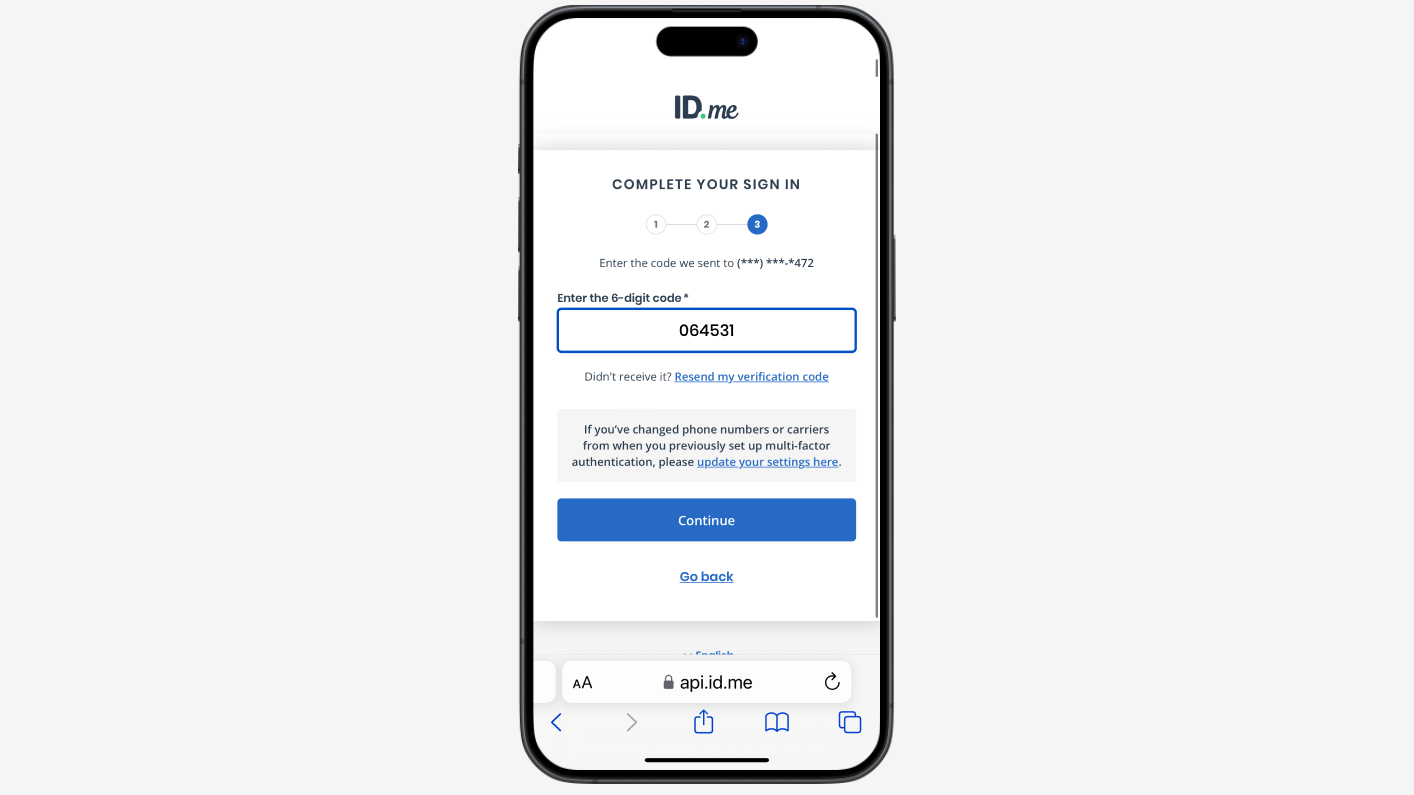
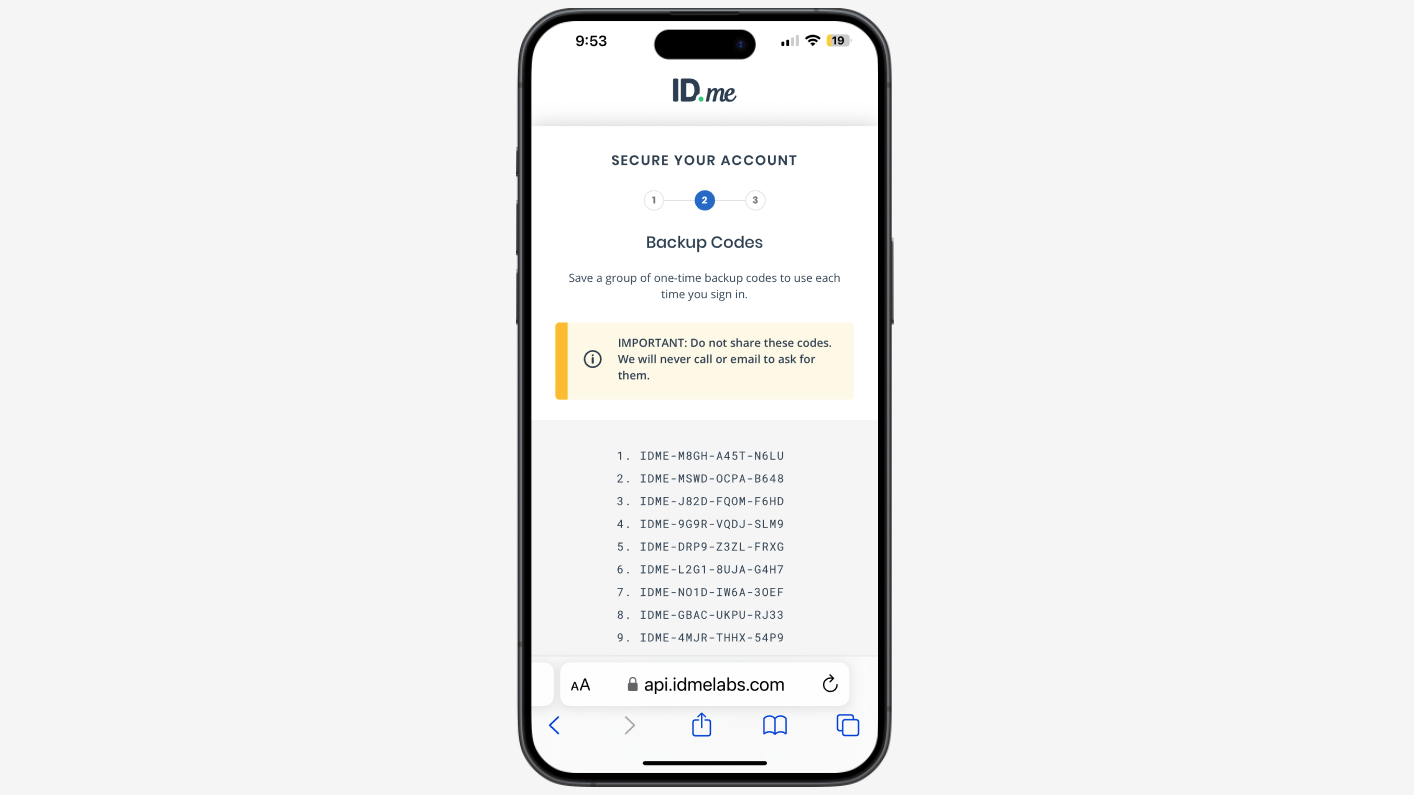
Authentication flows and MFA options
Here you can find what the ID.me Multi-Factor Authentication user experience looks like today:
Use cases
Here you can find example ID.me use cases: